
ABOUT THE COMPANY
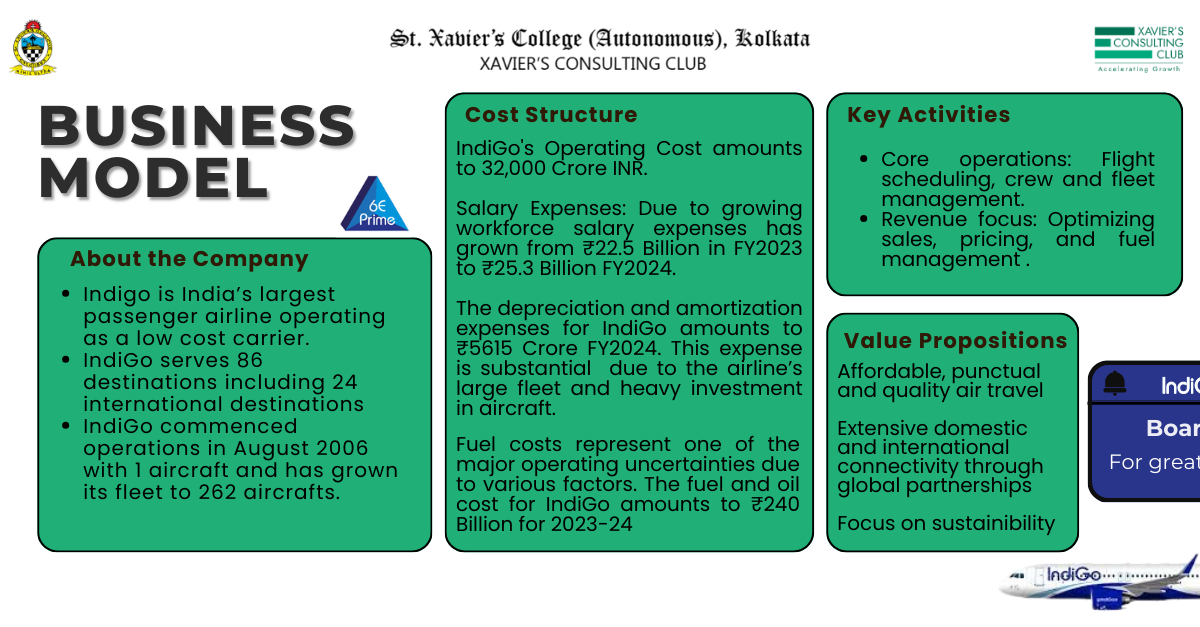
Indigo is India’s largest passenger airline operating as a low cost carrier. IndiGo serves 86 destinations including 24 international destinations IndiGo commenced operations in August 2006 with 1 aircraft and has grown its fleet to 262 aircrafts.
COST STRUCTURE
Fuel Expenses: Fuel costs represent one of the major operating uncertainties, which is affected by the number of flights undertaken, cost of fuel, and the type of aircraft. There are also fluctuations in fuel prices depending on the international markets.
Operational Costs: These include the day-to-day costs necessary for running the airline and ensuring smooth operations such as marketing, sales, crew training and ground handling.
Salaries and Expenses: IndiGo Airlines has shown a year-over-year increase in expenses from 2019 to 2024, largely due to a growing workforce and operational expansion. Specifically, salary and employee benefit expenses have grown to support IndiGo’s scale-up in fleet size and route offerings. Here’s a quick breakdown of IndiGo’s expenses across recent years:
Depreciation and Amortization expenses: The depreciation and amortization expenses for IndiGo from 2019 to 2024 were substantial due to the airline’s large fleet and heavy investment in aircraft. Here’s a breakdown of the figures (in ₹ crore) from available reports:
KEY ACTIVITIES
Flight operations:These include scheduling, crew management, on time performance assurance, and daily administration of local and international flight services.
Fleet Management: Purchasing, preserving, and modernizing aircraft to ensure compliance with safety regulations and operating efficiency.
Revenue management: Increasing profitability by optimizing flight capacity, seat distribution, and price.
VALUE PROPOSITION
IndiGo Airlines’ value proposition revolves around its commitment to providing a seamless, affordable, and reliable travel experience. Drawing from its 2024 presentation, the key elements of its value proposition are as follows:
Relentless commitment to Reliability and Punctuality: Known for its industry-leading on-time performance, IndiGo ensures dependable schedules, catering to the needs of time-sensitive travelers.
Expanding reach into International destinations: Indigo is constantly working towards expanding its reach and providing its service into international waters via its codeshare partnership with 8 leading global airlines.
Focus on Sustainability: Committed to reducing its environmental footprint, IndiGo invests in fuel-efficient aircraft and sustainable practices, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly travel.These elements underscore IndiGo’s position as a trusted leader in the aviation industry, delivering value through cost-efficiency, customer satisfaction, and a forward-looking approach.
REVENUE STREAMS
Overview of Revenue Model
IndiGo operates on a low-cost carrier business model. This model is characterized by a focus on cost efficiency and simplicity of operations. IndiGo achieves this by primarily using a single type of aircraft – the Airbus A320, which allows for better management of maintenance and operational costs. The airline also maximizes aircraft utilization by maintaining quick turnaround times and high-frequency operations. Further, IndiGo follows a point-to-point network model, flying directly between destinations without stopovers, which significantly reduces travel time and operational costs.
Revenue Model:
IndiGo’s revenue model is multi-faceted, with the main source of income being ticket sales. The airline’s low-cost model allows it to offer competitive fares, attracting a high volume of passengers and thereby driving revenue. In addition to ticket sales, IndiGo also generates revenue from ancillary sources such as baggage fees, in-flight meals, seat selection charges, and priority check-in. The airline also earns through its cargo operations, IndiGo CarGo, which provides domestic and international cargo services. Moreover, IndiGo has a loyalty program, ‘6E Rewards’, which not only ensures customer retention but also contributes to the revenue through its membership fees.
Revenue for FY 2023-24
InterGlobe Aviation reported record consolidated total income of ₹71,231.16 crore, up 27.5% year-on-year (y-o-y), and record net profit of ₹8,172.46 crore during the fiscal, against a net loss of ₹305.78 crore a year earlier.
Passenger ticket revenue
Passenger ticket revenue increased by 26.3% from `481,743.71 million in FY 2023 to `608,227.74 million in FY 2024.
Revenue from ancillary products and services
Revenue from ancillary products and services primarily include cargo, excess baggage, special service requests, ticket modification and cancellation, in-flight sales, and tours. Revenue from ancillary products and services increased by 20.9% from `54,415.21 million in FY 2023 to `65,789.01 million in FY 2024.
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) activities help organizations acquire, extend, and retain profitable customers. Indigo Airlines implements various CRM practices aimed at enhancing customer satisfaction, particularly for middle and lower-middle-class travelers. These initiatives include:
1. 6C Membership Scheme: Provides frequent flyers a 10% discount on ticket base rates.
3. Partial Payment Schemes: Customers from Citibank and HDFC can make partial payments or use EMI options.
4. Call Centers: 24/7 multilingual customer support.
KEY PARTNERSHIPS
In its LCC model, IndiGo relies heavily on various strategic partnerships which ensure operational efficiency, cost control, and an enhanced customer experience. These partnerships are important in its business model as they enable the airline to focus on core operations while outsourcing supplementary services and resources with the help of other businesses.
Aircraft Manufacturers (Airbus):Partnership Role: IndiGo has a long-standing relationship with Airbus, primarily operating the Airbus A320 family of aircraft. This standardized fleet helps IndiGo achieve cost efficiencies in training, maintenance, and operations.
Codeshare Agreements: A codeshare flight is one in which one carrier markets and the other operates. They are a result of an agreement between two carriers to sell seats on each other’s flights with the aim to offer its customers a large variety of destinations to choose. Indigo has codeshare partnerships with- Air France,American British Airways, KLM, Malaysia Airlines, Qantas, Qatar Airways,Turkish Airlines,Virgin Atlantic,Japan Airlines. It cooperates with travel-related third-parties such as MakeMyTrip and GDS like Amadeus in order to enhance its ticket sale avenues.
KEY RESOURCES
Aircraft Fleet: IndiGo’s fleet of efficient, modern planes ensures lower fuel and maintenance costs.
Workforce: The airline employs trained staff for flight operations, maintenance, and customer service.
Technology & IT Infrastructure: Strong digital presence, including an efficient website and mobile app for bookings and customer management
MARKETING STRATEGIES USED
Indigo Airlines adopts a comprehensive marketing mix, encompassing Product, Price, Place, and Promotion, to position itself as a leader in the low-cost air travel industry.
Product: Affordable Air Travel
The core product offered by Indigo Airlines revolves around providing low-cost air travel options to its customers. The airline strives for efficiency and cost reduction to offer affordable fares to a wide range of travelers. Indigo emphasizes operational excellence and streamlined processes to deliver a positive customer experience.
Price: Strategic Pricing
Indigo Airlines strategically prices its tickets to target price-conscious travelers. The airline offers competitive fares that appeal to budget-conscious consumers while maintaining quality service and reliability. By adopting a value-driven pricing strategy, Indigo ensures that its customers receive affordable air travel options without compromising on their expectations.
Place: Extensive Network and Distribution Channels
Indigo Airlines has established an extensive network of destinations to cater to a diverse customer base. The airline connects major cities and tier 1 as well as tier 2 cities, ensuring easy accessibility for its customers. Additionally, Indigo employs multiple distribution channels, both online and offline, to facilitate seamless ticket booking and enhance customer convenience.
Promotion: Low-Cost Marketing Campaigns
Indigo Airlines promotes its brand through low-cost marketing campaigns and advertisements. The airline focuses on cost-effective marketing strategies that effectively reach its target audience. By leveraging various marketing channels, including social media platforms and traditional advertising methods, Indigo creates brand awareness and drives customer engagement.
SOURCE

